Ultimate Guide to Ignition Coil Testing and Repair
If you've heard the saying, 'An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure,' then you understand the essence of maintaining your ignition coils.
But what if your vehicle suddenly displays erratic behavior, and you suspect the ignition coil might be the culprit? Understanding the intricacies of testing and repairing ignition coils could save you time, money, and unnecessary stress.
By mastering these essential skills, you not only ensure your vehicle's reliability but also gain a deeper insight into its inner workings.
Key Takeaways
- Different types of ignition coils have varying materials and designs for specific applications.
- Ignition coil maintenance varies with coil type; newer designs require less upkeep.
- Testing ignition coils involves measuring primary and secondary circuit resistances accurately.
- Recognizing symptoms of failing coils promptly is crucial to prevent engine damage and maintain optimal performance.
Types of Ignition Coils
When identifying the types of ignition coils used in automotive systems, it's crucial to understand the distinct characteristics and functions of distributor ignition coils, block ignition coils, pencil coils/stick coils, plug top coils/coil-on-plug, and ignition coil rails.
Ignition coil materials play a vital role in performance. Distributor ignition coils were historically made of materials like oil-filled canisters with points and a capacitor. Block ignition coils are often constructed with modern epoxy materials, enhancing durability and heat dissipation. Pencil coils/stick coils, commonly composed of materials like silicone and high-temperature plastics, offer efficient ignition and precise spark timing. Plug top coils/coil-on-plug systems utilize high-quality materials like silicone and magnetic steel to improve performance and reliability.
Regarding maintenance and lifespan, distributor ignition coils required regular maintenance due to their intricate design, while block ignition coils have longer lifespans due to simpler configurations. Pencil coils/stick coils and plug top coils/coil-on-plug setups generally have extended lifespans and require minimal maintenance, making them favorable choices for many automotive applications.
Testing Ignition Coils
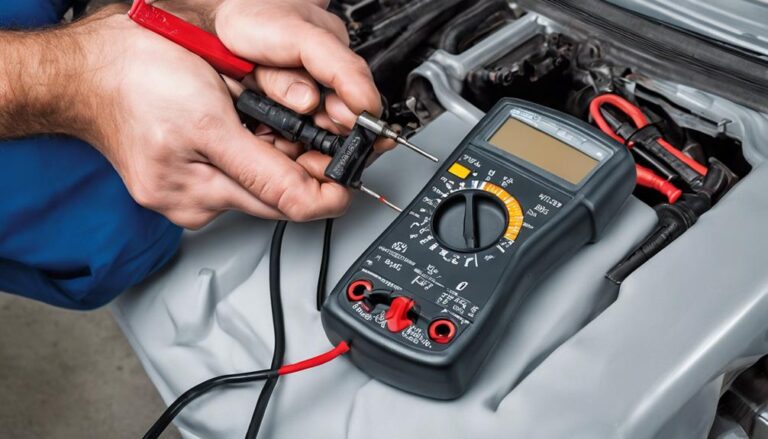
To accurately assess the functionality of your ignition coils, employ an ohmmeter to measure primary and secondary circuit resistance. Primary circuit resistance for most ignition coils should typically fall between 0.7 to 1.7 ohms, while secondary circuit resistance should be within 6,000 to 8,000 ohms for proper coil operation. By testing the ignition coil resistance, you can effectively diagnose engine issues and avoid unnecessary part replacements. Refer to the service manual or online resources for specific resistance values and testing procedures tailored to your vehicle's ignition coils. When conducting these tests, understanding advanced troubleshooting techniques and interpreting resistance readings correctly are essential to ensure accurate results.
| Resistance Type | Ideal Range | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Circuit Resistance | 0.7 – 1.7 ohms | Measure of primary winding health |
| Secondary Circuit Resistance | 6,000 – 8,000 ohms | Indicates secondary winding integrity |
Common Symptoms of Failing Coils
Experiencing engine misfires, rough idling, and hesitation during acceleration are common indicators of failing ignition coils. These symptoms can significantly impact your vehicle's performance, leading to reduced fuel efficiency and potential damage to other engine components. Ignition coil issues not only affect how your engine runs but can also shorten its longevity if left unresolved.
Additionally, a check engine light appearing on your dashboard could signal potential problems with the ignition coils. Ignoring these warning signs may result in difficulty starting your vehicle, stalling, or even backfiring, highlighting the importance of promptly addressing any suspected coil issues.
To maintain optimal engine health and performance, it's crucial to be aware of these symptoms and address them promptly. Regular maintenance checks, along with troubleshooting techniques, can help in detecting and resolving ignition coil issues early, ensuring your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently.
How to Diagnose Ignition Coil Issues
Upon observing common symptoms such as engine misfires or rough idling, diagnosing ignition coil issues involves conducting specific tests to pinpoint the source of the problem accurately.
To troubleshoot ignition coil problems effectively, understanding coil resistance is crucial. Testing the primary and secondary circuits for resistance with a multimeter can reveal if the coil is functioning within the manufacturer's specifications.
Additionally, performing spark tests using spark plug testers can confirm the ignition coil's functionality by checking if it produces a strong spark. It's essential to inspect the ignition coil for any physical damage or signs of wear, as these can also contribute to performance issues.
Repairing and Replacing Ignition Coils
When addressing issues with ignition coils, it's essential to thoroughly assess the condition of the components before proceeding with repairs or replacements. Ignition coil maintenance plays a crucial role in ensuring longevity and optimal engine performance. If one ignition coil is found to be faulty, it's recommended to replace all coils to prevent further damage and maintain efficiency. When considering repair or replacement, the choice between aftermarket and OEM coils is vital. While aftermarket coils may be more affordable, using OEM coils is advised to prevent severe damage and ensure the ignition system's effectiveness.
Driving with a bad ignition coil should be avoided as it can lead to additional issues. Replacement costs for ignition coils can vary depending on the vehicle's make and model. Investing in quality, authentic parts is key to the overall health of the ignition system. By prioritizing proper maintenance and using the right components, you can prolong the life of your ignition system and avoid costly repairs down the line.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Best Way to Test an Ignition Coil?
To test an ignition coil effectively, start by checking voltage measurement at the spark plug. Conduct bench testing on the secondary winding. Ensure accuracy in diagnosis and potential repair for optimal engine performance.
How Do You Diagnose a Bad Ignition Coil?
When diagnosing a bad ignition coil, consider symptoms like misfires. Troubleshoot by testing for spark using a spark plug tester. Use an OBD II scanner for pinpointing issues. Inspect for physical damage. Test resistance with a multimeter.
Can You Repair a Broken Ignition Coil?
You can't repair a broken ignition coil due to its sealed design and complex internal parts. DIY repair techniques can risk further damage. Ignition coil lifespan varies, but replacement is the recommended solution for optimal engine performance.
How Do You Check Primary Resistance on an Ignition Coil?
To check primary resistance on an ignition coil, set your multimeter to ohms and connect the leads to the primary terminals. Ensure accuracy in measurement for troubleshooting. If resistance falls within 0.7-1.7 ohms, your coil is likely in good condition.
Conclusion
Now that you've mastered the art of ignition coil testing and repair, you hold the key to unlocking your vehicle's full potential.
Just like a skilled mechanic fine-tuning a high-performance engine, you have the knowledge and expertise to ensure your car runs smoothly and efficiently.
So go ahead, rev up your engine with confidence, knowing that you have the power to keep your ignition system firing on all cylinders.