How to Read a Pressure Gauge
To read a pressure gauge, check the needle position and match it to the corresponding pressure unit indicated on the gauge scale. Pressure gauges are a commonly used instrument to measure the pressure of liquids and gases in various industrial and commercial settings.
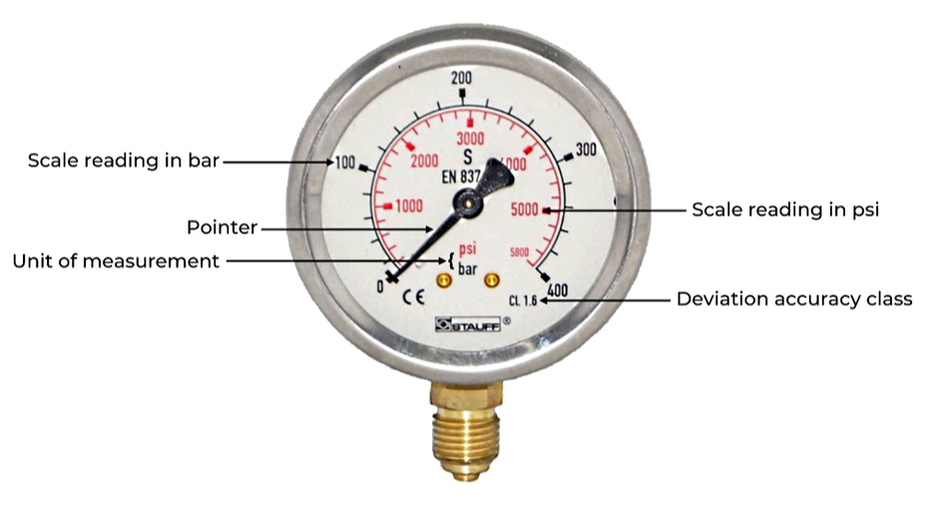
Understanding how to read a pressure gauge is crucial to ensuring accurate measurements and maintaining proper operational conditions. To correctly read a pressure gauge, start by checking the position of the needle on the gauge face. The needle points to the pressure level being measured.
Next, locate the scale on the gauge face and match the needle position to the corresponding pressure unit indicated. Pressure gauges may display measurements in various units such as pounds per square inch (psi), bars, or kilopascals (kPa). It is essential to double-check that the unit matches your requirements. By following these simple steps, you can effectively read a pressure gauge and gather precise pressure readings for your specific application.

Credit: www.rfshydraulics.com
Importance Of Reading Pressure Gauges
The proper reading of pressure gauges plays a crucial role in maintaining the safety and efficiency of various systems and processes. Whether it’s in industrial machinery, HVAC systems, or automotive applications, understanding the readings on pressure gauges is vital for preventing potential hazards, maintaining equipment performance, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Safety Precautions
Prior to interpreting pressure gauge readings, it’s essential to adhere to certain safety precautions to avoid potential risks and injuries. Always ensure that the equipment is properly grounded and that appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is worn when dealing with pressurized systems.
Types Of Pressure Gauges
There are several types of pressure gauges commonly used in different applications, each with its unique features:
- Bourdon tube gauges
- Digital pressure gauges
- Dial pressure gauges
- Diaphragm pressure gauges
- Capacitance pressure gauges
Understanding the specific type of pressure gauge being used is essential for accurate interpretation and reliable performance.
Credit: m.youtube.com
Understanding Pressure Gauge Components
When it comes to reading a pressure gauge accurately, it is essential to understand its various components. Each part plays a crucial role in providing accurate measurements and ensuring accurate readings. In this section, we will explore two important components of a pressure gauge: the dial or face and the pointer or needle.
Dial Or Face
The dial or face is the visual component of the pressure gauge that displays the pressure measurement. It typically consists of a circular disk with a printed scale or numerical values that represent different pressure levels. The scale can be in pounds per square inch (psi), bar, or any other unit of pressure measurement.
Pointer Or Needle
The pointer or needle is attached to the center of the dial and indicates the pressure being measured. It is usually a thin, metal arrow or needle that moves along the scale as the pressure changes. The position of the pointer corresponds to the pressure being exerted, allowing the user to read the precise pressure value.
Understanding the dial or face and the pointer or needle of a pressure gauge is vital in accurately interpreting its readings. By carefully observing the dial and tracking the movement of the pointer, you can determine the pressure being measured. This knowledge is particularly crucial in critical applications where precise pressure measurements are necessary for safety and optimal performance.
Reading And Interpreting The Pressure
Learn to interpret pressure by reading a gauge accurately. Understand the gauge markings and units for precise pressure measurement. Mastering this skill is essential for various industries and applications.
Reading and interpreting the pressure shown on a gauge is essential for proper equipment operation and maintenance. By understanding the pressure readings, you can quickly identify any abnormalities or potential issues. In this section, we will discuss the steps to read and interpret the pressure gauge accurately.Normal Operating Range
The normal operating range of a pressure gauge refers to the expected pressure values under normal working conditions. It provides a baseline to compare the current pressure reading against. The normal range typically varies based on the specific equipment or system you are monitoring. To determine the normal operating range, refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines or equipment specifications.Units Of Measurement
Pressure gauges may display pressure readings in different units of measurements. Some common units include pounds per square inch (psi), bars, kilopascals (kPa), and atmospheres (atm). It is crucial to understand the units being used on the gauge to ensure accurate interpretation of the pressure readings. Here’s a quick reference table for converting between some of the most frequently used units:| Unit of Measurement | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|
| psi | 1 psi = 0.0689 bar = 6.895 kPa = 0.068 atm |
| bar | 1 bar = 14.504 psi = 100 kPa = 0.987 atm |
| kPa | 1 kPa = 0.145 psi = 0.01 bar = 0.01 atm |
| atm | 1 atm = 14.696 psi = 1.013 bar = 101.325 kPa |
- Ensure the gauge is correctly installed and connected to the system or equipment.
- Observe the pressure gauge closely, making note of the scale and increments.
- Note the current pressure reading indicated by the needle or marker on the gauge.
- Compare the reading to the normal operating range for the system or equipment.
- If the reading falls within the normal range, the equipment is operating as expected. However, if the reading exceeds or falls below the normal range, further investigation or action may be required.
Calibrating And Maintaining Pressure Gauges
When it comes to maintaining a pressure gauge, it is crucial to ensure that it is accurately calibrated and properly maintained. Proper calibration and maintenance not only help in accurate readings but also extend the lifespan of the gauge, ensuring it performs optimally for a longer period. Let’s delve into the essential aspects of calibrating and maintaining pressure gauges.
Calibration Methods
Pressure gauges should be calibrated regularly using various methods to ensure accurate readings. Here are some prevalent calibration methods:
- Deadweight Tester: Uses known weights to apply pressure and compare the readings with the gauge’s measurements.
- Comparison Calibration: Involves comparing the pressure gauge with a standard reference gauge to verify its accuracy.
- Digital Pressure Calibrator: Utilizes digital tools to generate known pressures and verify the gauge’s readings.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and accuracy of pressure gauges. Consider these maintenance tips to ensure optimal performance:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the gauge for any signs of damage or wear, such as cracks, corrosion, or inaccurate dial readings.
- Seal Checks: Ensure that the seals and gaskets are intact and not deteriorating, as leaks can affect the gauge’s accuracy.
- Calibration Schedule: Establish a routine calibration schedule to validate the gauge’s accuracy and make adjustments as necessary.
- Environmental Protection: Protect the gauge from extreme temperatures and harsh environments to prevent damage and maintain accuracy.
- Proper Handling: Handle the gauge with care to avoid impacts or mishandling that could affect its calibration and accuracy.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
Many people miss the importance of the zero reading on a pressure gauge, which leads to inaccurate measurements.
Not considering environmental factors like temperature and humidity can affect the pressure reading significantly.

Credit: blog.wika.us
Frequently Asked Questions On How To Read A Pressure Gauge
How Do You Read A Psi Pressure Gauge?
To read a psi pressure gauge, look at the needle’s position for the pressure reading. Each tick mark represents a specific pressure level. The needle points to the current pressure. Always ensure the gauge is properly calibrated for accurate readings.
Regularly inspect the gauge for any damage or wear.
How Do You Read A Pressure Gauge Accuracy?
To read a pressure gauge accurately, ensure the gauge is clean and properly calibrated. Check that the pointer is aligned with zero. Read the measurement at eye level and consider any pressure fluctuations. Avoid rough handling to maintain gauge accuracy.
How Do You Measure Pressure With A Pressure Gauge?
To measure pressure with a pressure gauge, connect the gauge to the pressure source, ensuring it’s securely attached. Read the pressure value on the gauge’s display, which indicates the force exerted by the fluid or gas. Make sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for accurate measurements.
What Is The Unit Of Reading For Pressure Gauge?
The unit of reading for a pressure gauge is typically pounds per square inch (psi).
How Do You Read A Pressure Gauge Accurately?
To read a pressure gauge accurately, check the needle position against the scale for precise measurements.
Why Is It Important To Know How To Read A Pressure Gauge?
Understanding pressure gauge readings helps monitor equipment performance and prevent potential safety risks.
What Are The Common Units Of Measurement On A Pressure Gauge?
Common units on a pressure gauge are PSI (pounds per square inch) and bar for different applications.
Conclusion
In essence, reading a pressure gauge is a fundamental skill that anyone working with machinery should possess. Understanding the pressure measurement is crucial for maintaining equipment and ensuring safe operations. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you will be well equipped to read pressure gauges accurately and effectively in various work environments.


