How Often To Change Hydraulic Fluid
In the intricate machinery of hydraulic systems, the fluid serves as a vital component that enables the transfer of power and facilitates smooth operation. Like a well-orchestrated symphony, each element must harmonize to optimize performance and prevent potential breakdowns. The regular changing of hydraulic fluid is an essential maintenance practice aimed at ensuring system longevity and efficiency. This article explores the recommended frequency for changing hydraulic fluid, taking into account various factors that influence its lifespan. By adhering to established guidelines and recognizing signs indicating necessary change, operators can mitigate potential risks associated with degraded fluid quality. Furthermore, understanding the proper procedure for fluid replacement allows for seamless execution without compromising system integrity. Ultimately, consistent adherence to routine changes confers numerous benefits upon hydraulic systems, including enhanced operational reliability and extended service life. Through clear explanations and technical precision, this article provides valuable insights on how often one should change hydraulic fluid in order to sustain optimal system performance.
Importance of Regularly Changing Hydraulic Fluid
Regularly changing hydraulic fluid is crucial to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of hydraulic systems, as it helps to remove contaminants and maintain optimal lubrication. Clean hydraulic fluid offers several benefits. Firstly, it promotes efficient operation by minimizing friction between moving parts. This reduces wear and tear on components, which in turn extends their lifespan. Additionally, clean fluid enhances the system’s overall performance by ensuring smooth and precise movement of pistons, valves, and other hydraulic components. It also prevents the formation of sludge or varnish that can clog passages or restrict flow within the system.
Neglecting regular fluid maintenance can have severe consequences on hydraulic systems. Over time, contaminants such as dirt particles, metal shavings, or water can accumulate in the fluid. These contaminants can cause abrasive damage to internal surfaces and seals within the system. Increased friction due to contaminated fluid not only accelerates component wear but also leads to reduced efficiency and decreased power output.
Understanding the lifespan of hydraulic fluid is essential for effective maintenance practices. By comprehending factors such as operating conditions, usage intensity, and type of equipment being used, one can determine an appropriate schedule for fluid replacement. Transitioning into the subsequent section about ‘understanding the lifespan of hydraulic fluid,’ it is important to consider these factors when establishing a maintenance routine."
Understanding the Lifespan of Hydraulic Fluid
Periodic maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of hydraulic systems, necessitating a thorough understanding of the lifespan of the fluid employed in these systems. Hydraulic fluid storage plays a significant role in determining its lifespan. Proper storage conditions are essential to prevent degradation and contamination of the fluid. Ideally, hydraulic fluids should be stored in clean, sealed containers away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
Contamination is another factor that affects the lifespan of hydraulic fluid. Contaminants such as dirt, water, air, and chemicals can negatively impact the fluid’s performance and accelerate its degradation. These contaminants can enter the system through various ways, including improper handling or storage practices, equipment wear and tear, or external factors like dust or water ingress.
The effects of contamination on hydraulic fluid include reduced lubrication properties, increased friction and wear on components, decreased heat transfer efficiency, formation of sludge or varnish deposits, and compromised system reliability. Over time, these issues can lead to decreased system efficiency and potential failure.
Understanding the lifespan of hydraulic fluid is crucial for determining how often it needs to be changed. Factors such as operating conditions (temperature extremes, heavy loads), type of equipment (pumps with higher demands), and desired system reliability all play a role in determining the frequency at which hydraulic fluid changes are necessary.
Factors that Determine the Frequency of Fluid Changes
The frequency of fluid changes in hydraulic systems is determined by a variety of factors, including operating conditions, equipment demands, and desired system reliability. Factors affecting fluid change frequency include the type of hydraulic system, the quality and cleanliness of the fluid, and the severity of operating conditions.
Firstly, different types of hydraulic systems have varying requirements for fluid changes. For example, high-performance systems that operate under extreme temperatures or pressures may require more frequent fluid changes to maintain optimal performance. On the other hand, less demanding systems may be able to go longer between fluid changes.
Secondly, the quality and cleanliness of the hydraulic fluid also play a crucial role in determining its lifespan. Contamination from dirt, debris, or water can accelerate wear on components and reduce the effectiveness of additives in the fluid. Regular monitoring and analysis can help determine when it is necessary to change the fluid.
Lastly, common misconceptions about hydraulic fluid lifespan can lead to unnecessary or inadequate maintenance practices. Some operators believe that as long as there are no visible signs of contamination or degradation in the fluid, it does not need to be changed. However, this approach fails to account for internal wear and tear on components that may not be immediately apparent.
In conclusion, understanding these factors affecting fluid change frequency is essential for proper maintenance of hydraulic systems. By considering operating conditions, equipment demands, and desired system reliability alongside misconceptions about lifespan expectations will help determine appropriate guidelines for changing hydraulic fluids without compromising system performance or longevity
Recommended Guidelines for Changing Hydraulic Fluid
An appropriate guideline for determining when to replace hydraulic fluid is akin to following the footsteps of a seasoned tracker, relying on a combination of regular monitoring, analysis, and adherence to manufacturer recommendations. By following these guidelines for hydraulic maintenance, operators can ensure optimal performance and longevity of their hydraulic systems. The best practices for fluid replacement are as follows:
-
Regular Fluid Analysis: Conduct routine oil analysis to monitor the condition of the hydraulic fluid. This includes analyzing key parameters such as viscosity, water content, acidity level, and contamination levels.
-
Operating Conditions: Consider the severity of operating conditions when determining fluid replacement intervals. Factors such as high temperatures, heavy loads, or harsh environments may require more frequent changes.
-
Manufacturer Recommendations: Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific recommendations on fluid change intervals based on system design and components used.
-
Maintenance Records: Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities including fluid changes. This helps track usage patterns and provides valuable information for future decision-making.
Following these guidelines ensures that hydraulic systems operate at peak efficiency while minimizing the risk of component failure due to degraded or contaminated fluid. In the next section, we will explore signs that indicate it’s time to change the fluid without compromising system performance.
Signs that Indicate it’s Time to Change the Fluid
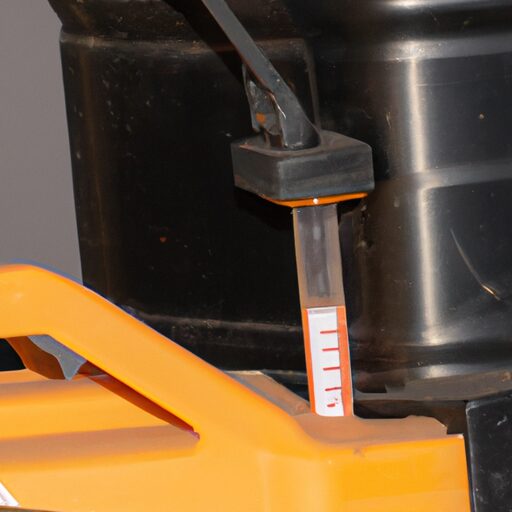
Indicators of fluid degradation and the need for replacement can be observed through various signs in hydraulic systems. One key indicator for when to change hydraulic fluid is the presence of contaminants. These contaminants, such as dirt, debris, or water, can enter the system and cause damage to sensitive components over time. Another sign is a change in color or consistency of the fluid. Hydraulic fluids that appear darker or have a milky appearance may indicate contamination or degradation. Additionally, if there is an increase in temperature within the system, it could be a sign that the fluid has lost its ability to lubricate and cool effectively.
Other indicators for hydraulic fluid replacement include excessive noise or vibration during operation. This can suggest that the fluid has become contaminated with air bubbles or solid particles, which can hinder its performance. Furthermore, if there is a noticeable decrease in system efficiency or responsiveness, it may be time to change the hydraulic fluid as it could no longer meet the demands of the system.
In conclusion, recognizing these indicators for hydraulic fluid replacement is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity of hydraulic systems. By monitoring signs such as contaminants, changes in color/consistency, increased temperature, excessive noise/vibration, and decreased efficiency/responsiveness, one can determine when it’s necessary to replace the hydraulic fluid. Transitioning into proper procedure for changing hydraulic fluid involves following specific guidelines to maintain system integrity without compromising its functionality.
Proper Procedure for Changing Hydraulic Fluid
Once the signs indicating that it is time to change the hydraulic fluid have been recognized, it is crucial to follow the proper procedure for changing the fluid. Hydraulic fluid maintenance is a critical aspect of ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of hydraulic systems. The process involves several steps that need to be executed with precision.
Firstly, it is essential to locate and access the hydraulic fluid reservoir. This may require removing covers or panels, depending on the specific system design. Once accessed, care must be taken to clean any dirt or debris from around the fill cap before opening it.
Next, a suitable container should be prepared to collect the old hydraulic fluid as it is drained from the system. The drain plug can then be loosened, allowing the fluid to flow out completely. It is important to ensure that all of the old fluid has been drained before proceeding.
After draining, new hydraulic fluid can be added through the designated fill port until it reaches appropriate levels. It should be noted that different systems may require specific types or grades of hydraulic fluids, so consulting manufacturer guidelines or industry recommendations is essential.
In conclusion, following these steps for changing hydraulic fluid will contribute significantly to maintaining an efficient and reliable hydraulic system. Regularly changing hydraulic fluids not only extends its lifespan but also enhances overall performance and reduces equipment downtime due to potential failures caused by degraded fluids.
Benefits of Regularly Changing Hydraulic Fluid
Regularly changing the hydraulic fluid can significantly enhance the performance and lifespan of the hydraulic system, resulting in minimized equipment downtime and improved overall efficiency. One of the benefits of clean fluid is that it helps to maintain proper lubrication within the system. Hydraulic systems rely on the fluid for lubricating moving parts, reducing friction, and preventing wear and tear. When the fluid becomes contaminated with dirt, debris, or other contaminants, it loses its ability to effectively lubricate the components. This can lead to increased friction and heat generation, which can cause premature component failure.
Moreover, regularly changing hydraulic fluid also helps to remove any accumulated contaminants from the system. Over time, particles such as dirt, metal shavings, or moisture can enter the hydraulic system and contaminate the fluid. These contaminants can clog filters, valves, and other components, impeding their proper functioning. By regularly replacing the hydraulic fluid with clean fluid through a thorough flushing process as recommended by manufacturers’ guidelines, these contaminants are effectively removed from the system.
The impact of using contaminated hydraulic fluid can be detrimental to both productivity and cost-efficiency. Contaminated fluid poses a higher risk of component failures due to increased wear and tear caused by inadequate lubrication or blockages in critical passages. This results in more frequent maintenance requirements and unplanned equipment downtime.
In conclusion, regular changes of hydraulic fluid offer numerous benefits for maintaining optimal performance in a hydraulic system. Clean fluid ensures proper lubrication while removing accumulated contaminants that could impair functionality. By adhering to recommended maintenance practices regarding hydraulic fluids’ replacement frequency outlined by manufacturers’ guidelines or industry standards relevant to specific applications would result in extended equipment lifespan while minimizing potential disruptions due to unexpected breakdowns or inefficient operation caused by contaminated fluids
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use any type of hydraulic fluid for my equipment?
Hydraulic fluid compatibility depends on the equipment’s specifications. It is essential to use the recommended hydraulic fluid types as specified by the manufacturer to ensure optimal performance and prevent damage to the equipment.
How can I determine the condition of my hydraulic fluid without laboratory testing?
Determining contamination levels in hydraulic fluid can be done without laboratory testing. Monitoring fluid color and consistency is crucial. Changes in color or the presence of particles indicate potential issues and may necessitate changing the fluid.
Can I extend the lifespan of my hydraulic fluid by adding additives?
Adding additives to hydraulic fluid may extend its lifespan by improving its performance and protecting against wear and corrosion. However, the effectiveness of additives depends on various factors such as the type of additive used and the operating conditions.
Is it necessary to change hydraulic fluid if the equipment is not used frequently?
In order to ensure optimal equipment performance, it is necessary to maintain the quality of hydraulic fluid even if the equipment is not used frequently. Regularly changing hydraulic fluid helps prevent degradation and maintains its effectiveness during storage.
Are there any environmental considerations when disposing of used hydraulic fluid?
Disposal methods for used hydraulic fluid should prioritize environmental impact. Proper disposal techniques include recycling, reusing, or treating the fluid to remove contaminants before disposal in accordance with local regulations to minimize harm to ecosystems and human health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, regularly changing hydraulic fluid is crucial for maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of hydraulic systems. The lifespan of hydraulic fluid can vary depending on various factors such as operating temperature, system cleanliness, and load conditions. Following recommended guidelines for fluid changes and being attentive to signs indicating the need for a change are essential. By adhering to proper procedures for changing hydraulic fluid, operators can ensure the system’s efficiency and prevent costly repairs. Ultimately, prioritizing regular maintenance and fluid changes will contribute to the smooth operation of hydraulic systems in various industries.