Engine Diagnostic Tips for Beginners: A Comprehensive Guide
When your car's check engine light flickers on, it's natural to feel a sense of unease. Understanding what lies beneath that ominous warning can provide a sense of control and potentially save you from costly repairs down the road.
By mastering a few key engine diagnostic tips, you'll be equipped to decipher those mysterious codes and pinpoint issues before they escalate. So, let's uncover some essential insights that will empower you to tackle engine troubles with confidence.
Key Takeaways
- Recognize engine misfire symptoms for timely diagnostics.
- Utilize essential tools like OBD-II scanners and multimeters.
- Interpret check engine codes to pinpoint specific faults.
- Conduct visual inspections and compression tests for engine health assessment.
Common Engine Problems and Symptoms
Recognizing common engine problems and their associated symptoms is crucial for beginners in engine diagnostics. Troubleshooting techniques play a vital role in identifying issues like engine misfires. Diagnostic challenges may arise when faced with symptoms such as rough idling, stalling, and hesitation during acceleration. These signs often indicate misfiring, which can lead to poor power output and decreased fuel efficiency.
When you encounter a check engine light illuminating, loss of power, or decreased fuel economy, it could be indicative of potential engine issues. Excessive oil consumption, hard starting, and poor performance are also red flags that shouldn't be overlooked. Understanding that misfires, poor power output, and decreased fuel efficiency are common symptoms of engine problems will help you approach diagnostics more effectively.
Basic Tools for Engine Diagnostics
To effectively conduct engine diagnostics, beginners should ensure they have essential tools such as OBD-II scanners, multimeters, compression testers, and vacuum gauges at their disposal. Each tool serves a specific purpose in diagnosing engine issues. Here's a quick look at these tools and their functions:
| Tool | Function |
|---|---|
| OBD-II Scanner | Retrieves trouble codes from the vehicle's computer system for analysis |
| Multimeter | Tests electrical components like sensors, switches, and wiring |
| Compression Tester | Assesses the condition of the engine's cylinders and piston rings |
| Vacuum Gauge | Assists in diagnosing issues related to engine vacuum leaks or performance |
When comparing diagnostic tools, understanding their unique functions is crucial for effective troubleshooting techniques. The OBD-II scanner provides insights into the vehicle's computer system, while the multimeter helps in testing electrical components. Compression testers evaluate engine cylinder conditions, and vacuum gauges pinpoint issues related to vacuum leaks or engine performance. By utilizing these tools effectively, beginners can streamline their diagnostic process and identify engine problems accurately.
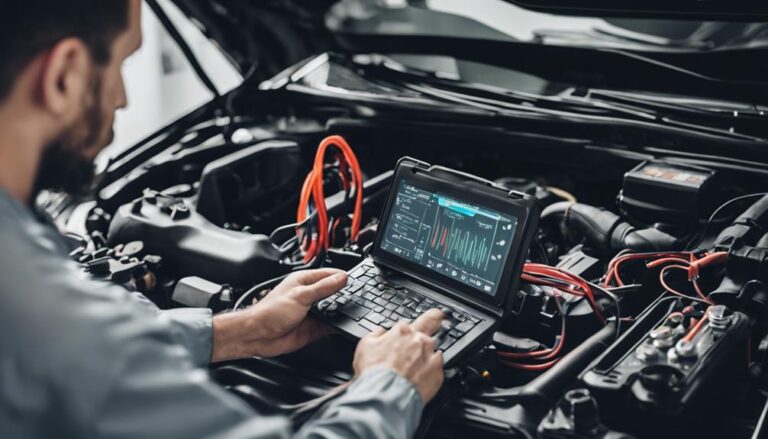
Understanding Check Engine Codes
Understanding check engine codes involves decoding the alphanumeric combinations stored in your vehicle's onboard computer system to pinpoint specific engine or system faults. To effectively interpret these codes and troubleshoot engine issues, consider the following techniques and strategies:
- Diagnostic Scan Tools: Utilize a diagnostic scan tool or code reader to retrieve the codes stored in the engine control unit (ECU).
- Code Interpretation Techniques: Learn the meaning of common codes such as P0300 for random/multiple cylinder misfire and P0171 for a lean fuel mixture.
- Troubleshooting Strategies: Use the identified codes as a starting point for diagnosing the root cause of the engine problem.
- Early Problem Identification: Understanding check engine codes allows for early detection of issues, enabling timely action to maintain engine health.
Performing a Visual Inspection
Upon inspecting your vehicle's engine bay, meticulously assess for any oil leaks, corrosion, or damaged components to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Common signs of issues during a visual inspection include spotting oil puddles under the engine, visible rust on metal parts, or cracked hoses. Troubleshooting techniques involve checking for loose wires, disconnected hoses, and signs of wear on belts and pulleys.
Look closely at the battery terminals for any corrosion buildup that could hinder proper electrical flow. Inspect the air filter for clogs or dirt accumulation, as this can impact engine performance by restricting airflow.
Additionally, verify that all fluid levels, such as oil, coolant, and brake fluid, are at the recommended levels. Addressing these visual cues promptly can prevent potential breakdowns and maintain your engine's health for the long run.
Steps to Conduct a Compression Test
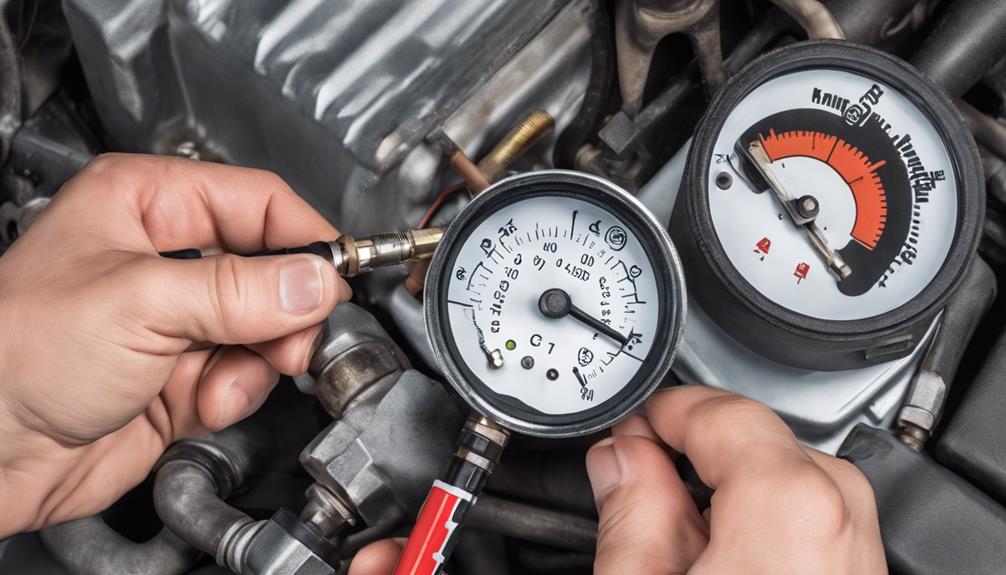

Begin by preparing your vehicle for the compression test by ensuring the engine is at operating temperature and the ignition system is disabled to prevent accidental starts. Conducting a compression test is essential for effective compression troubleshooting techniques and accurate engine performance evaluation.
Follow these steps to perform a compression test:
- Step 1: Remove all the spark plugs from the engine to allow easy cranking.
- Step 2: Connect a compression gauge to the first cylinder and hold the throttle wide open.
- Step 3: Disable the ignition system to prevent the engine from starting and crank the engine a few times to get a stable reading on the gauge.
- Step 4: Repeat the process for each cylinder and compare the pressure readings.
Low compression levels in one or more cylinders indicate potential issues requiring further inspection and repair to maintain optimal engine performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the 7 Steps to Automotive Diagnoses?
To diagnose automotive issues, consult the owner, connect tools to the computer, and analyze DTCs. Skilled interpretation is crucial for accurate identification. A detailed report explains the vehicle's condition and recommends repair steps.
How Do I Run a Full Diagnostic on My Car?
To run a full car diagnostic, start by using basic tools like an OBD-II scanner. Look for common issues such as misfires or sensor problems. Conduct tests on sensors, compression, and fuel pressure for accurate pinpointing.
How Do I Know What's Wrong With My Engine?
To diagnose engine issues, pay attention to common symptoms like warning lights, strange noises, and fluid leaks. Use troubleshooting techniques such as checking fluids, inspecting belts, and using diagnostic tools for a comprehensive understanding of your engine's health.
How Do You Learn to Diagnose Car Problems?
To learn car problem diagnosis, get hands-on. Utilize online resources for guidance. Practice with tools and symptoms. Your skills will grow through experience. Don't hesitate to seek help when needed. You got this!
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering engine diagnostics is crucial for maintaining your vehicle's health and performance. By familiarizing yourself with common issues, utilizing basic tools, and understanding check engine codes, you can prevent major repairs and ensure your engine runs smoothly.
Remember, a little inspection and maintenance goes a long way in keeping your vehicle running like a well-oiled machine. Happy diagnosing!